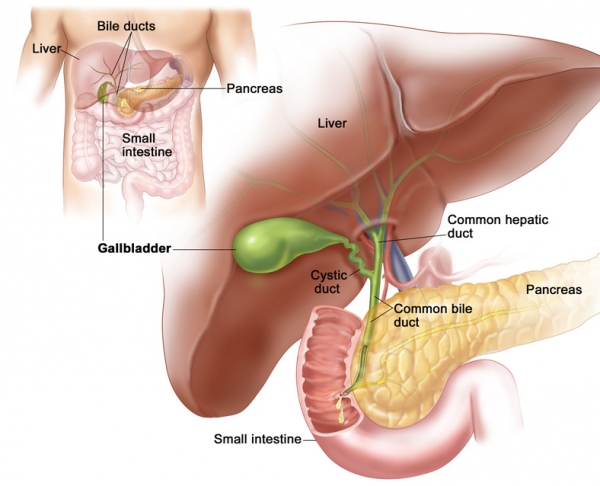
In discussing the Gall bladder, In TCM we begin with the Liver. Your liver is an amazing thing – it is the largest organ in your body, and it is tasked with a number of principle functions that regulate your overall health. At any given moment, the liver contains about a 13% of all the blood in your body. Two types of blood are delivered to the liver throughout the day – oxygenated blood from the heart (25%), to refresh and nourish the liver cells, and blood that is filled with products of digestion, coming from the stomach and small intestine (75%). This blood is filtered by your liver, which metabolizes its molecular components into the appropriate ratio of sugars, proteins, and lipids your body needs at any given time of the day. As the stomach and small intestine are the “doorways” for all things you ingest (good and bad) it is also the job of the liver up to determine what the body needs to get rid of, and what form the waste products and toxins need to be in to be moved out of the body in the safest way possible. The liver produces bile, a fluid that both aids in digestion of fats and transports waste products into the large intestine. It stores the bile in the gall bladder, which releases it according to what the liver needs at a particular time of the day. The smoother the flow of bile, the more quickly you can metabolize and absorb food and get waste products out of your body.
Role of the Gall Bladder
Under normal physiologic conditions, the gallbladder gradually collects bile that is being pumped out of the liver and expands to hold the bile, and then releases most of the collected bile, via the bile duct, into the duodenum (upper part of the small intestine) upon stimulus from eating. The bile combines with the partially digested food material: starches are digested during chewing, proteins upon mixing with stomach acids. In the duodenum, bile helps solubilize the fats in the food to make digestion easier, and digestive enzymes from the pancreas, including a group of lipases to break down fats, complete most of the digestive process.The Gallbladder is classified both as a Fu and as an extraordinary organ since it both stores and secretes bile. As the reservoir for Heat and Dampness in the body, the Gall Bladder is responsible for absorbing excesses from the Liver. The Liver function in Chinese medicine is direct smooth flow, specifically of Qi, Blood, digestion, and emotion. Liver depression means lack of free flow, and its specific cause is unfulfilled desires. Depression of free flow creates Heat (specifically, depressive Heat), and excess Heat can be dumped into the Gall Bladder. Gall Bladder dysfunction characterized by Heat is thought of in Chinese medicine as arising from prolonged stagnation, leading to resentment and festering anger (the festering quality arises from Dampness, produced by the Spleen).
Gall Stones (Cholelithiasis)
Gallstones can lurk inside your gallbladder. Many people have gallstones and never know it. Virtually all gallstones are formed within the gallbladder, which stores bile excreted from the liver. Bile is a solution composed of water, bile salts, lecithin, cholesterol and some other small solutes. Cholesterol stones are the most common type of stone. Normally, bile acids, lecithin, and phospholipids help to maintain cholesterol as a solute. Changes in the relative concentration of these components may cause precipitation from solution and formation of a nest, When bile is supersaturated with cholesterol, it crystallizes and forms a nidus for stone formation.
Whilst the stones can exist without causing issues, often stone(s) can block the cystic ducts. A stone blocking the opening from the gallbladder or cystic duct usually produces abdominal pain that feels like cramping. If the stone does not pass into the duodenum, but continues to block the cystic duct, acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) manifests causing abdominal pain, tenderness, fever, chills, nausea and vomitting. If the common bile duct is blocked for a substantial period of time, certain bacteria may find their way up behind the stone and grow in the stagnant bile producing symptoms of cholangitis (Infection of the Bile ducts), which is a serious condition that typically requires hospitalization for treatment. Pancreatitis (inflamation of the Pancreas) can also be as a result of gallstones stopping pancreatic enzymes from traveling to the small intestine and forcing them back into the pancreas. The enzymes then begin to irritate the cells of the pancreas, causing pancreatitis.
In TCM, the fundamental etiology of gallstones and cholecystitis is typically Damp-Heat. Cholecystitis is characterized by Damp Heat in the Gallbladder and gallstone is characterized by Damp Heat drying up fluid in the Gallbladder.
Factors in Gall Stone Formation
Factors contributing to Gallstone formation include :
- being overweight or obese
- eating a diet that’s high in fat or cholesterol
- rapid weight loss within a short period of time
- eating diet that’s low in fiber
- having diabetes mellitus
- Pregnancy or the use of birth control pills
First Gallstone Attack – wait and see approach
One-third of all patients with gallstones never experience a second attack. For this reason, many doctors advise an attitude of “wait and see” after the first episode. Changing the diet or following a sensible weight loss plan may be the only treatments required.
Stone Shrinking Herbs
The ability to reduce the size of stones using herbs or other methods is not an established fact. However, certain Chinese herbs have been selected as stone-dissolving herbs. There is one traditional-style formula that is reputed to dissolve stones, called San Jin Tang, or the Decoction of Three Golds. The three golds are jin qian cao, hai jin sha, and ji nei jin. The formula was devised at the Shuguang Hospital of the Shanghai College of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Stone Expelling Herbs
 |
The herbs used in the strong stone expelling decoctions, as described earlier, have been formulated into easy to use tableted patent formulas that are given at much lower dosage. For example, Lidan Pian (Gallbladder Normalizing Tablets) and Lidan Paishi Pian are patent remedies recommended for cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. These tablets have a milder action than the corresponding decoctions and may be used in a complete program of gallstone therapy for treating smaller sized stones or mild gallbladder inflammation. Treatment time with stone expelling formulas is usually 8-12 months, though excretion of gallstones may begin to occur within days.
Acupuncture for Gallstones
The most commonly used points for the treatment of this condition are: qimen (LV-14) and riyue (GB-24), juque (CV-14).(local points to relieve pain and stagnation) yanglingquan (GB-34), qiuxu (GB-40), and zusanli (ST-36) neiguan (PC-6) and zhigou (TB-6), (dannangxue), just below GB-34 (about 1-2 cun lower). Qimen and riyue are the front mu points of the liver and gallbladder meridians respectively; zhigou and yanglingquan can relieve hypochondriac pain, while zusanli helps strengthen the spleen and disperse dampness-heat. Dannangxue is feature point for Gallbladder disharmony
Integrated Therapy Approach for GallStones and improved Gall bladder Functions
1. A regular daily exercise program. This should include meditative exercises (Taiji, Yoga or Qigong) as they can regulate the emotions and more vigorous methods depending on the age of the patient
2. Give yourself time to heal emotionally Chinese medicine reminds us that often those with gallbladder distress are likely to be feeling anger, frustration, and resentment. Do something that will make you feel well: go for a long hike, relax in the sun, rebuild your positive energy supply.
3. A nutrition plan that is high in fibre, including fruits, vegetables, beans and wholegrain products.
4. Avoid greasy foods or Reduce the intake of butter, lard, oils, Full cream or full fat dairy products (Milk, cheese) , snacks, crisps, pasteries, nuts, puddings, pies, ice cream, sauces, meats and processed meats. Sometimes the use of Coconut oil as an alternative as it is very easy on the gallbladder because it contains mostly short and medium chained fatty acids, which do not require pancreatic enzymes or bile salts to digest. You can use it as a substitute for cooking oil.
5. Drink plenty of fluid including water or herbal teas. Warm lemon juice in the mornings is helpful.
6. A regular meal schedule that encourages the gallbladder to fill completely between meals. This means minimizing or eliminate snacking (which is an approach contrary to some dietary recommendations for managing eating disorders and some other health problems). Must take care when eating food containing fats, you must learn to chew well, eat slowly and in moderation.
7. Daily consumption of stone dissolving substances/herbal medicines, including the Sanjin Tang and, if required, bile salts.
8. Consumption of herbs that promote bile flow (mainly herbs that treat qi stagnation and damp-heat).
9. Acupuncture therapy to regulate circulation of qi, purge the gallbladder, and alleviate pain in the gallbladder region
What if your Gallbladder was surgically removed
After removal of the Gall Bladder other organs progressively replace or circumvent its function. You may have loose or watery stools after gallbladder removal. This diarrhea occurs because removing a gallbladder involves rerouting the bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile no longer goes through the gallbladder after surgery and it becomes less concentrated. The result is a laxative effect that causes diarrhea. If you eat a diet lower in fats, less bile will be released. Examples of dietary steps you can take (similarly to that of the integrated therapy nutrition plan) include:
- Reduce your intake of fats. Choose low-fat foods whenever possible. Avoid high-fat, greasy, and fried foods.
- Add fiber to your diet. Extra fiber can make your bowel movements less liquid. Try to add only a serving of fiber at a time to prevent gas that can occur from eating excess fiber.
- Avoid foods and drinks known to cause diarrhea, such as caffeine, high-fat dairy products, and very sweet foods.
- Eat several small meals per day instead of large meals. Smaller meals are easier for the body to digest.